The Comprehensive Guide to Digital Design Software

This guide describes the main categories of digital design software, provides the benefits and drawbacks for each type of software and highlights some of the available software on the market.
CAD
CAD (Computer-aided Design) software is used by architects, designers, engineers and more to create precision drawings and technical illustrations. It can be used to create both 2D and 3D models and is standard documentation tool in the industry and design process.

Benefits:
- Produce accurate designs and drawings to scale
- Shallow learning curve - easy to train staff with a strong existing knowledge base and industry experts
- Reference consultant drawings for collaboration between disciplines and within a team
- Excellent file compatible with 3D and BIM programs. Drawings can be imported/exported from one program to another
Drawbacks:
- Drawings are independent and not linked across a project.
- Additional work in coordinating, checking drawings and reducing discrepancy errors throughout a project.
- Need to implement policies and checks to ensure drawing styles and office standards are adhered to across projects.
Software
- AutoCAD – Used mainly for 2D and 3D design and drafting, AutoCAD is used by drafters, engineers, surveyors and architects to design and document projects accurately and efficiently. It is an industry standard.
- Microstation – Microstation is an information modelling environment to design and document 2D and 3D designs. It is used mostly for architecture, engineering and construction as it favours dimension-driven design, allowing users to create accurate drawings and geometry for their project.
3D Modelling
3D Modelling software focus on geometry creation and rendering - allowing the design of 3D objects from the conceptual phase to detailed design most often with the ability to prepare your model for fabrication. They are used in multiple disciplines including Product Design, Architecture, Engineering and Animation. 3D modellers offers maximum design flexibility with geometry being able to be constructed and manipulated with little constraint.

Benefits:
- Designers can work with flexible geometries, making it easy designs anything you can imagine.
- Most 3D modellers have a parametric engine to automate geometry construction
- Enables rapid iterations and exploration of potential design solutions in 3D
- Produces file formats that are compatible with 3D Printers, Laser Cutters and CNC robotics.
Drawbacks:
- You may encounter different types of geometry (Mesh, Subdivision or Nurbs). These are fundamentally different geometry types and may limit the modification of geometry when working between applications.
- Documentation is not automated and there are a series of processes and software typically involved to create high quality orthographic drawings (plans, sections, elevations) from 3D models.
Software
- Rhino - Rhino is known for its ability to create versatile and accurate 3D models using NURBS surfaces. It’s fast and easy-to-use interface allows plugins that permit drawing, analysis, digital prototyping and fabrication of each project. The Rhino software is compatible with most other design platforms, with designs being able to be transferred to and from other design, drafting, CAM, engineering, analysis, rendering, animation, and illustration software.
- 3DS Max – 3DS Max is a professional 3D computer graphics program used for animations, design modelling, rendering images and is a tool for compositing solutions for games. 3DS Max is often the tool of choice for Architectural Rendering professionals and can accept geometry from the major CAD / BIM applications.
- Maya – Maya is a 3D computer animation software used for modelling, rendering, simulation, texturing and animation tools for artists, animators and modellers. You can perform advanced Character Modelling, Rigging and Texturing workflows and work with cutting edge dynamics including Fluids, Hair, Cloth and Particle Systems. Maya also has tools to produce Subdivision models to create organic characters or architectural forms and allows you to work with rigid and soft bodies to simulate collisions and dynamic systems.
- SketchUp – SketchUp is an easy-to-use 3D modelling software allowing you to generate 3D forms from simply drawing lines and shapes, and pushing / pulling them into 3D forms. It contains simple tools such as stretch, copy, rotate and paint to create quick, customisable 2D documents and 3D models. You can easily convert your 3D models into scaled drawings and documents using Sketchup’s Layout tool. The intuitive interface has made it popular tool for Architects.
BIM
Building Information Modelling (BIM) software allow the 3D modelling of buildings using tools that replicate real world element. A building can be designed using floor slabs, walls, doors, windows and roofs. Most importantly, the 2D drawings are generated from the 3D model, allowing you to edit the model in Plan, Elevation, Section or 3D and all views update concurrently. 3D visualization of a project and has the capacity to minimize errors due to human error and can identify any potential design clashes.
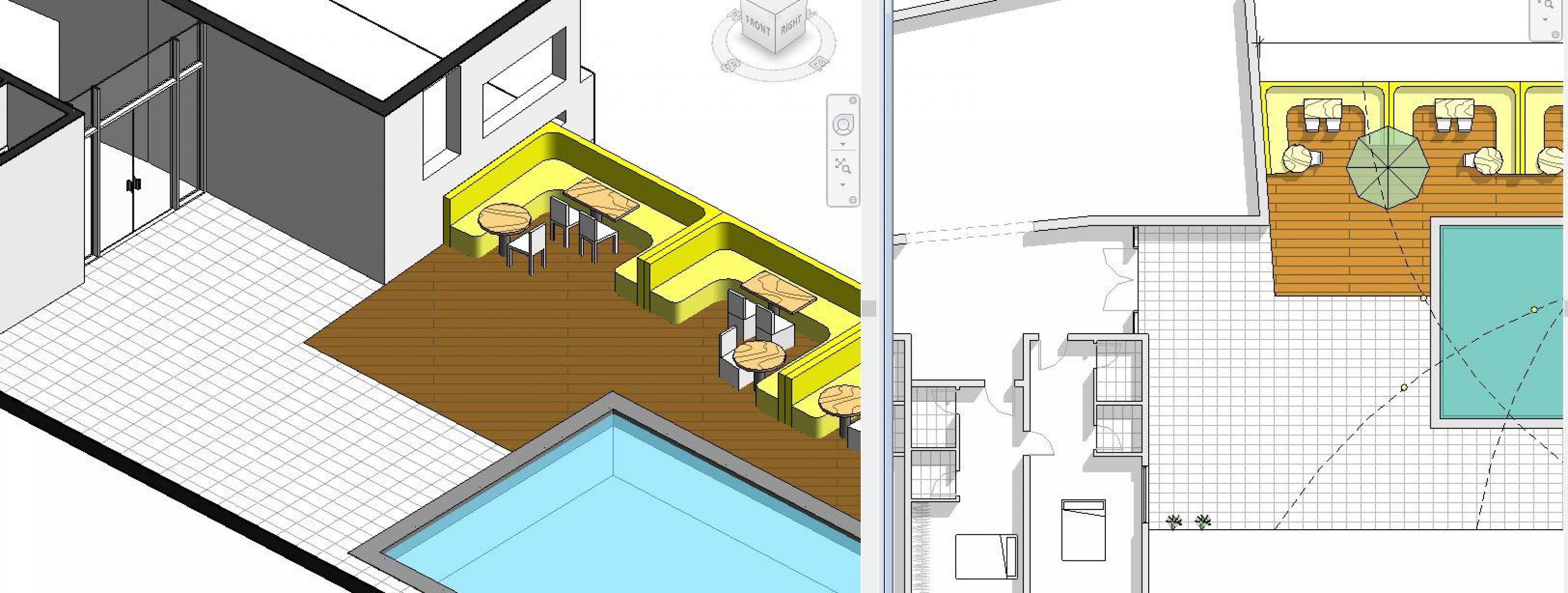
Benefits:
- BIM offers a collaborative design process, increased productivity and workflow efficiency.
- BIM is great for reducing errors and ensuring consistency across your project as you operate in an integrated 3D model where plans, sections, elevations and 3D views are all interrelated.
- You can produce detailed schedules and extract building data directly from the model.
- Post Construction, BIM can benefit owners / occupiers as the detailed model can be used for facilities management.
Drawbacks:
- Like all design software, the initial cost, training and implementation of BIM resources is expensive.
- BIM models can often be slow to update and re-load the model between team members, especially in larger projects.
- Complex geometries can be difficult to represent / integrate due to the rigid structure of a BIM model.
Software
- Revit – Revit software is designed specifically for a BIM workflow where it ranges from the concept state to construction. Revit models can be designed with precision with built-in tools available to enable team collaboration. Revit also has specific toolsets available for Structure and MEP engineers. Revit now comes with Dynamo standard which allows powerful visual scripting.
- ArchiCAD – ArchiCAD is used by architects, designs, engineers and buildings to design, document and collaborate on building projects. It is also used for visualisation and performance with options for accurate, live-feedback about your building design’s energy consumption. You can share an interactive BIM model using their cloud sharing app BIMX.
Parametric Modelling
Parametric Modelling offers a flexible, automated method to create complex design models. It permits a quick method to explore, iterate, change and test design models until an appropriate solution is found. Users can embed intelligence and constraints into their designs which can be both powerful and problematic. Geometry that is dependent on each other may reduce design errors further down the track but may also make editing difficult for those who did not create the model initially.
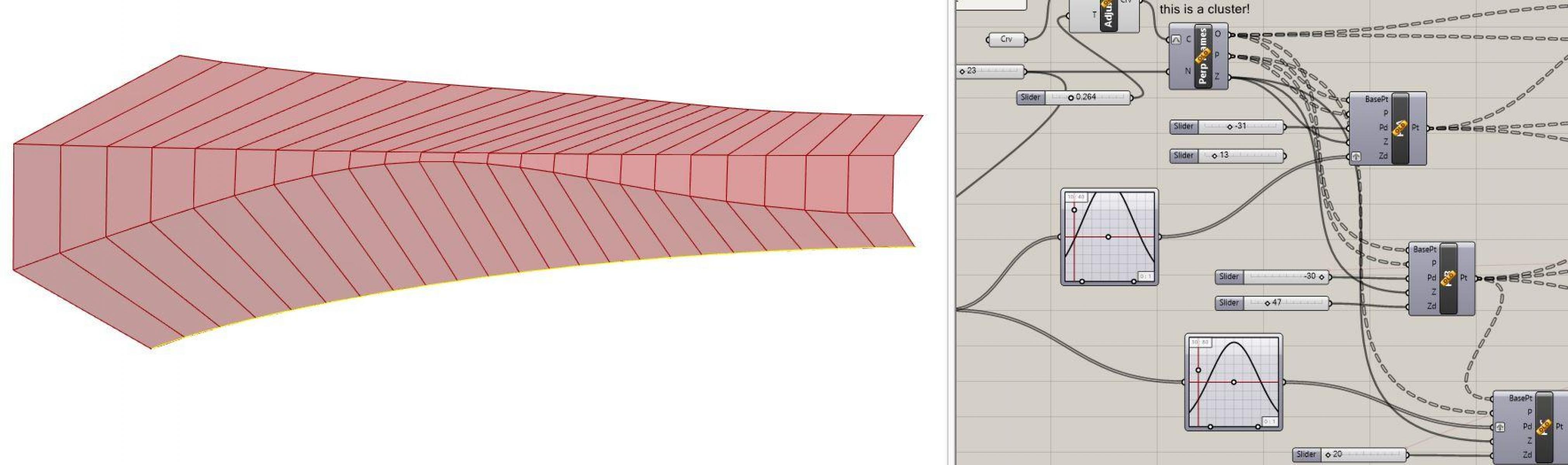
Benefits:
- Using Parametric Modelling you can embed intelligence into a design, allowing designers to easily re-use this intelligence through all stages of the product lifecycle.
- Create a variety of models with custom interfaces to tweak individual features within defined ranges
- Automatic updates to the model if changes are made to the design
Drawbacks:
- There is a steep learning curve for designers who must learn how to think programmatically
- Building constraints into the model can sometimes complicate the design process
- Model updates may take some time if you are working with complex geometry
- It may be difficult to adjust a model’s final geometry as it must be built into the chronological steps that combine to create the design
Software
- Grasshopper – Grasshopper is a graphical algorithm editor that is integrated with Rhino’s 3-D modelling tools. It requires no prior knowledge of programming or scripting but allows designers to build and generate data-driven forms using a visual programming language.
- Dynamo – Dynamo is a community-driven open source tool for graphical programming in design. It is plugin to the Revit software that extends BIM with the data and logic environment of a graphical algorithm editor.
Rendering
Architectural renders are useful to visualize a design concept, ranging from simple drawings to computer-generated images reflecting real-life situations. Video game engines are now available to designers and offer entirely new presentation possibilities. Whilst the visualization process may be time consuming and often tricky to find the right settings to perform the job (colour, lighting, framing, composition, angles to convey moods and more), the final image is a persuasive and key communication tool between the designer and end user.

Benefits:
- Architectural rendering is often a necessity- renderings can win competitions and commissions
- Three-dimensional spatial experiences provide opportunities to comprehensively explain projects and understand the experience of a building before it is built.
- Rendering can often inform the design process especially in regards to material selection.
- Rendering is a service that can be outsourced
Drawbacks:
- Architecture visualisation is a multi-step process that often requires the use of more than one software package.
- Rendering can be very time consuming.
- Need to source or create a library of materials and entourage element to produce photo-realistic renders
Software
- V-Ray – V-Ray is a rendering plug-in developed by Chaos Group for use in media, entertainment and design industries such as video game production, industrial design, product design and architecture. It is the most powerful rendering engine for artists and digital designers and contains all the lighting, shading, and rendering tools you need to create quick, professional, photoreal imagery and animation. V-Ray is fully integrated into your favourite 3D applications including 3DS Max, Maya, Rhino, SketchUp, Blender, Modo and Nuke.
- KeyShot – KeyShot is rendering program that allows you to create fast, accurate and amazing visuals. It has a real-time workflow so you can see material, lighting and environment changes instantly as you design and it includes scientifically accurate material and environment presets. KeyShot has integrated plugins for all the most popular 3D modelling software including Rhino, Revit, SketchUp, 3Ds Max, Fusion 360, Creo and Solidworks.
- Lumion – Lumion is visualisation software built specifically for Architects and enables designers to create videos and images without prior training. You can edit and rework your project in real time with fast rendering tools and options to create on-the-spot, customisable videos. It is fully compatible with your favourite software including SketchUp, Revit, Vectorworks and Allplan.
- Maxwell – Known for its quality and realism, Maxwell is a rendering software focused on lighting and contains a library of real-world materials with a minimal set-up time.
- Adobe Photoshop – Photoshop is known as the world’s best photo editing software with tools to create and enhance your photos, images, 3D artwork and more. Photoshop is typically used post-production to add in People, Trees and add visual enhancements to renders.
Analysis
It is now easier than ever to gather real-time analysis on the performance of a design with a range of analysis software emerging that plug directly into your design environment. These programs provide quick feedback for any current design.

Benefits:
- Get real time feedback during your design process with accurate data to achieve performance-driven design
Drawbacks:
- There is a limited range of software available to determine and extract architectural analytics from a design.
- There is also a steep learning curve for those who do not know how to use the programs available already
- Analytics can be time intensive to produce.
Software
- ArchiStarr – Archistarr introduces a suite of design analytics providing you the ability to assess the performance of your design across a range of environmental, configuration and design criteria. It also allows comparative design within your portfolio and benchmarking across the design database. ArchiStarr has plugins to integrate into your favourite CAD/BIM modelling workflows for real-time analysis as you design!
- Sefaira – Sefaira Architecture provides performance analysis within your 3D environment. It interprets models in real-time, delivering analysis and results while you design. The program makes it easy to understand how a building’s orientation, form and fenestration impacts performance and provides energy and daylighting feedback as you work. They currently support plugins in SketchUp and Revit.
- Ladybug + Honeybee - Ladybug and Honeybee are two open source environmental plugins for Grasshopper to help designers and engineers create an environmentally-conscious building design allowing sunlight, daylight and other environment analytics.
- Kangaroo – Kangaroo is a plugin to Grasshopper 3D that is a live Physics engine for interactive simulation, optimization and form-finding.
- Karamba - Karamba is another Grasshopper plugin that has parametric structural engineering tools to provide an accurate analysis of spatial trusses, frames and shells.
Summary
The software that the AEC industry is using has evolved from standard 2D drafting that has been fundamental to the profession to fully integrated 3D modelling environments that contain building information, design analytics and programmable interfaces. This brings a plethora of new tools and processes as you can see from this guide into the available technologies. These tools are allowing more complex designs, performance driven design, rapid prototyping and the move to mass customisation and digital fabrication of building elements.
If you would like to share your thoughts on our blog, we’d love to hear from you!
Get in touch with the ArchiStar Academy community via Facebook.
Posted on 20 Jan 2020
